|
|
PreCHECK
NSF SciSIP Grant #1952353 (PI: Bei Yu, co-PI: Jian Qin)
Understanding Press Release Exaggeration of Scientific Research |
Publications
|
Yu B, Wang J, Guo L, Li Y (2020) Measuring Correlation-to-Causation Exaggeration in Press Releases. COLING'2020.
[
PDF
|
source code
]
Mentioned by Ivan Oransky (co-founder of RetractionWatch) on
Twitter.
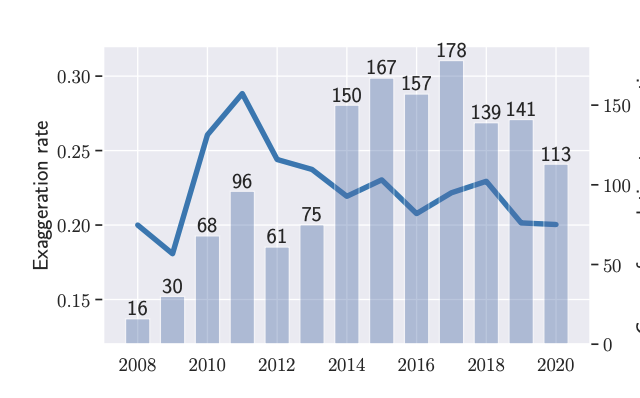
...22% of press releases made exaggerated causal claims from correlational findings...Furthermore, universities exaggerated more often than journal publishers by a ratio of 1.5 to 1. Encouragingly, the exaggeration rate has slightly decreased...
|
|
Wang J, Yu B (2021) News2PubMed: A Browser Extension for Linking Health News to Medical Literature. SIGIR'2021 (Demo paper)
[
PDF
|
Abstract
|
Demo
]
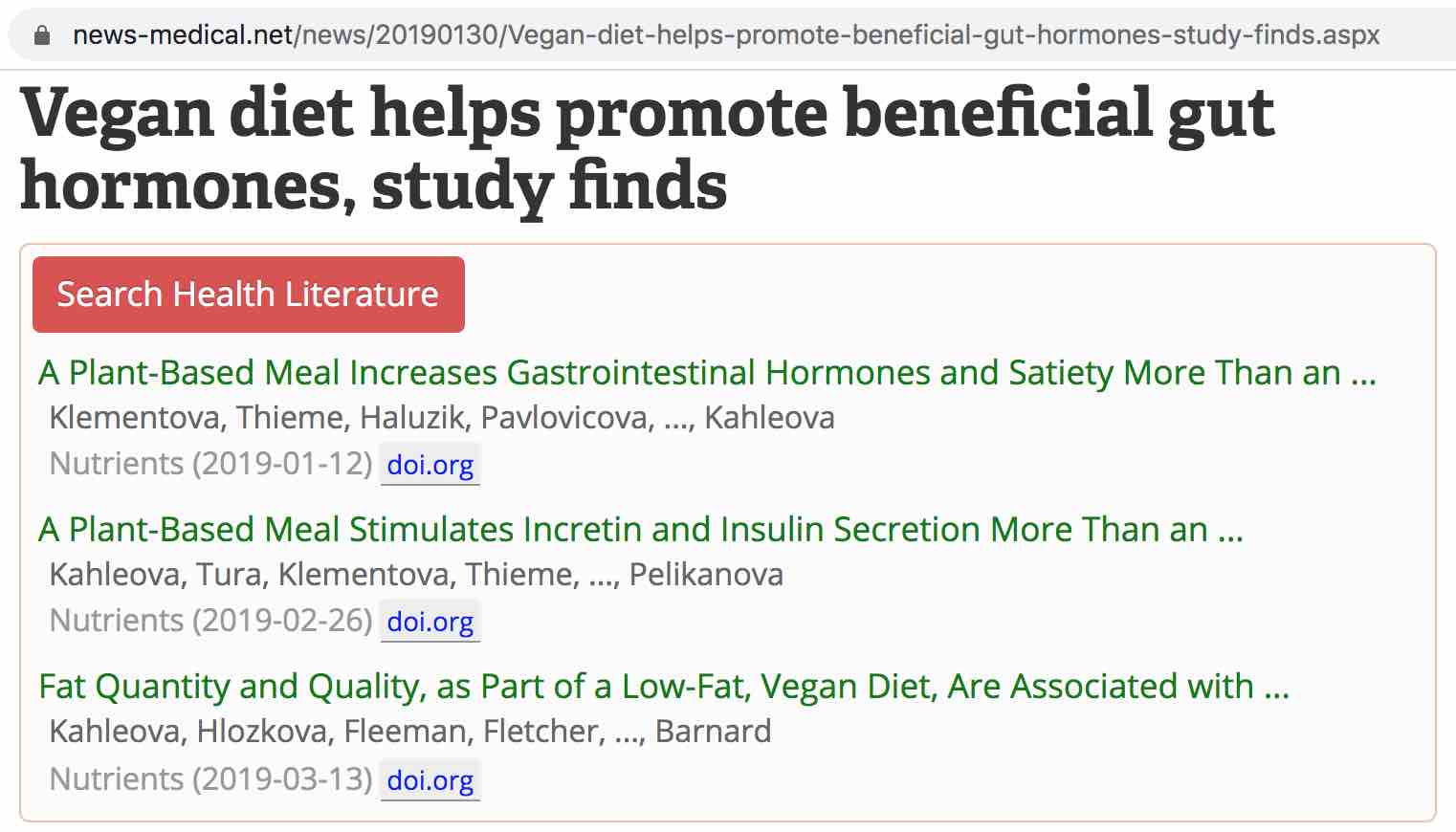
This demo system presents a browser extension that allows the reader of a health news article to quickly retrieve related medical/health research papers.
Wang J, Yu B (2021) Linking Health News to Research Literature. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06472 (Technical details)
Our approach was able to identify the corresponding research papers, with a top-1 accuracy of at least 0.97,
on 37,600 health-related press releases published on EurekAlert!.
|